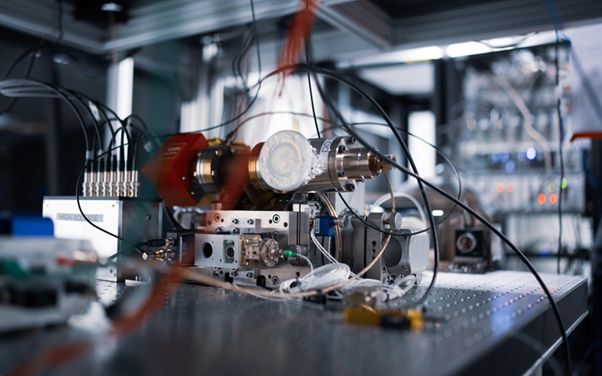
A pioneering MIKOK project has been launched at Warsaw University of Technology to develop a state-of-the-art quantum infrastructure using calcium ions. This is the first project of its kind in the country, which could open the door to revolutionary applications in cryptography, pharmaceuticals and business process optimization.

MIKOK project
The MIKOK project, whose full name is “Development of modular quantum computer infrastructure for special and military computing applications,” is underway at the Warsaw University of Technology. The consortium responsible for the project consists of the Warsaw University of Technology (leader), the Military University of Technology, the Military Institute of Armament Technology, the Silesian University of Technology and SONOVERO R&D. Together, they are striving to develop a prototype of a calcium ion-based (Ca⁺) quantum computer infrastructure.
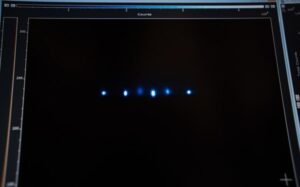
At the heart of the prototype is an ion trap in which calcium ions are placed. The process begins with the release of calcium atoms from the source material using a laser pulse. These atoms are then ionized and cooled by the laser, allowing them to be trapped in the ion trap. Thanks to the precise interaction of electromagnetic fields, the ions form a one-dimensional crystal, resembling a string of pearls. In this arrangement, each ion can act as a cubit – the basic unit of quantum information.

Utilization of Calcium Ions
The choice of calcium ions for the prototype is not random. Their energy levels are well defined, allowing precise control of quantum states. In addition, ion trapping technology is well developed and offers the stability necessary for complex quantum operations. This enables the realization of quantum gates – the basic elements of information processing in quantum computers.
Quantum computers have the potential to solve problems that are insurmountable for classical supercomputers. In the field of cryptography, they can contribute to the creation of new encryption methods and the breaking of existing security features. In pharmaceuticals, they can enable the simulation of complex chemical reactions, which will speed up the process of discovering new drugs. Optimization of logistics and financial processes are other areas where quantum computers may find application.